Expert Guide to the Rules of the Road when Driving in Europe

Driving in and around mainland Europe is a lot different to driving at home, with many laws and regulations – as well as other factors – that you need to be aware of. This Expert Guide covers the most important points you need to be aware of, and read in conjunction with our Expert Guide: Touring in mainland Europe, offers a great introduction, or refresh, for touring on the continent.
Please note that the information provided primarily applies to our key destination markets of France, Spain and Portugal, and is subject to change, so it’s always worth doing your own research for specific countries and circumstances before you travel.
The basics
Driving licence
You are permitted to drive in the EU if you have a photocard driving licence issued in the UK, but you may need an International Driving Permit (IDP) to drive in some EU countries and Norway if you have an older-style paper driving licence or a licence issued in Gibraltar, Guernsey, Jersey or the Isle of Man. We advise that you exchange any older-style licence for a photocard licence, which is readily recognised across Europe.
Worth Noting: On 16 December 2021 UK B only licence holders were all automatically given B+E entitlement. If you are one of these and intend to tow a car and caravan combination over 3,500kg while outside the UK you will need this detail on your physical driving licence to tow that heavier combination. Make sure your licence is updated in good time to avoid any issues.
Different countries may require different forms of International Driving Permit but the IDP itself is available from stores that use the Paypoint service, locations can be found here. Find out more by visiting gov website.
 Entitlement to tow combinations over 3,500kg (B+E) was added to B only driving licences in December 2021 – make sure your licence is updated before travelling
Entitlement to tow combinations over 3,500kg (B+E) was added to B only driving licences in December 2021 – make sure your licence is updated before travelling
Renewal of driving licences
UK drivers must renew their photocard driving licence with a new picture every ten years. We highly recommend you renew in plenty of time before the expiry date to avoid any delays when the DVLA processes your application.
Drivers who need to provide a medical report when renewing their licence (such as those approaching the age of 70 who want to retain their C1 licence category) should be prepared for it to take longer than a regular licence renewal.
Renewing online can help speed up the process but this isn’t currently possible for those driving a vehicle over 3,500kg. The authorities in Europe cannot check your details easily so you’ll need your physical driving licence with you while touring in mainland Europe.
Driving licences and car hire
If you are hiring a car or motorhome while you are away you will need to check what documentation you need to provide when collecting the vehicle. To share the details from your driving licence, request a code here.
For more information, including what your licence entitles you to drive, check out our guide on driving licences.
Tax and MOT
Your vehicle tax and MOT must always be up to date to legally drive abroad. If your MOT certificate is due to expire while you are away you will need to renew it before you leave the UK. Click here to check when your vehicle tax and MOT are due.
Caravans are not covered by MOT tests in the UK but you are still responsible for their roadworthiness, so we recommend they are regularly serviced, and tyres replaced every five to seven years from the date of manufacture. See our Experts Guides for motorhomes and campervans, caravans and trailers and unbraked trailers for more information.
Vehicle cross border sticker
You must display a UK sticker on the rear of your vehicle. If you have an old GB sticker, this must be covered or removed. In addition, a separate UK sticker must be displayed on the rear of your car and any towed trailers when travelling to Spain, Malta and Cyprus.
If your number plate includes the UK identifier with the union flag, you don’t need a separate UK sticker unless you’re visiting one of the countries mentioned above. For more details click here.
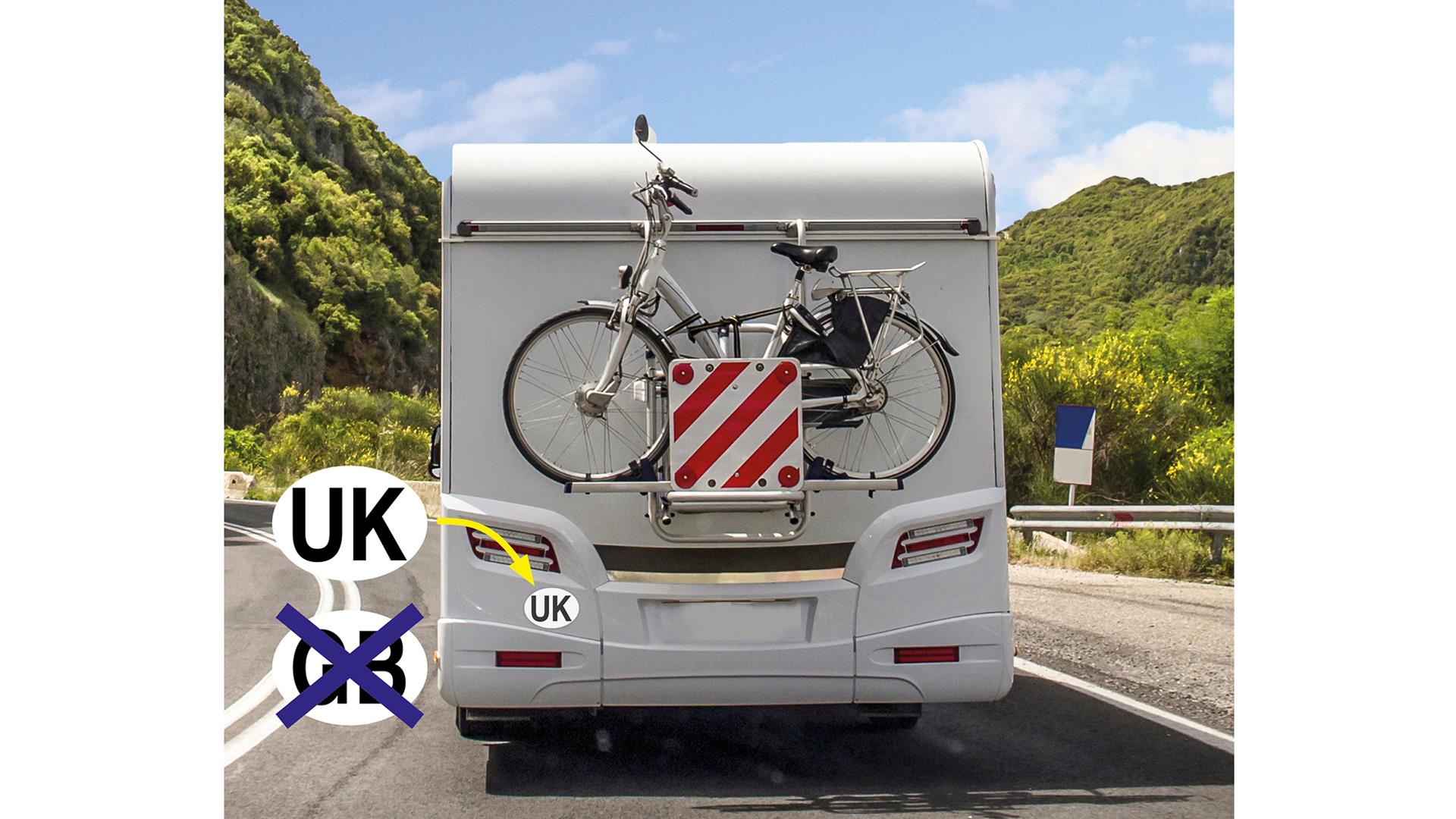 You must display a UK sticker on the rear of your vehicle – any old GB stickers must be covered or removed
You must display a UK sticker on the rear of your vehicle – any old GB stickers must be covered or removed
Insurance
Insurance green card
A green card is proof that you have vehicle insurance when driving abroad and is available from your insurer. UK residents no longer need a green card for car or trailer when travelling to the following countries:
- the EU (including Ireland)
- Andorra
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Iceland
- Liechtenstein
- Norway
- Serbia
- Switzerland
A green card may be needed for other countries – see the Government travel advice here for details.
If needed, your insurance provider will either post the green card to you (allow up to six weeks for it to arrive) or let you download one to print. Note, it does not need to be printed on green paper.
Vehicle insurance
You will need a minimum of third-party insurance cover for the countries you visit, which will cover any damage you do to others. Contact your motor insurance provider before taking your vehicle abroad, to confirm what level of cover you will have and what documents you need. Also check your camping unit remains fully covered while abroad, including if you leave it temporarily while it is on a pitch.
The Club’s insurance provider Club Care has more than 30 years’ experience in this field and can offer a range of services. For details visit the website or call 0800 124 4633.
Trailer insurance
A UK car insurance policy will cover your trailer (third party insurance cover only) when it is hitched to the towing vehicle. You must have informed your insurer of the towbar and display the same registration plate on your trailer as on the towing vehicle. You may want to arrange comprehensive insurance cover for the caravan or trailer itself and any equipment or valuables they contain. Club Care is a good option once again.
European Accident Statement (EAS)
Though not a legal requirement, this document is highly recommended, and can be obtained from your insurance company prior to taking your vehicle abroad. The document helps get an agreed statement of facts about an accident and can help with insurance claims, more details here.
Speed limits
Keep in mind that road signage for speed limits on the continent is in kilometres per hour (kmh). Built-up areas normally limit speed to 50kmh and many countries have lower speed limits for poor weather conditions. We recommend not exceeding UK speed limits even if allowed due to stability and excessive fuel consumption reasons. Below are some specific speed limits by country in kmh, displayed in the format: Motorways / Dual Carriageways / Other roads, for example 110kmh / 90kmh / 80kmh.
 Speed limits vary by road, country and even region
Speed limits vary by road, country and even region
France
Cars, campervans and motorhomes (including towed combinations up to 3,500kg): 130/110/80. Non-towing motorhomes over 3,500kg: 110/100/80.
If car and caravan combination is over 3,500kg the limits are 90/90/80.
*If towing a trailer or caravan heavier than the car a sliding scale of reduced speeds applies and also requires the use of speed limit stickers, but since this would be illegal in the UK it can be discounted.
Portugal
Cars: 120/100/90. There is no clear advice for motorhomes over 3,500kg. Towing: 100/80/70.
Spain
Car speed limits: 120/100/90, motorhome: 100/90/90. Towing with a car or motorhome: 80/80/70. Motorhomes over 3,500kg: 90/80/80.
Germany
130/100/100, but 60kmh in built-up areas. Certain stretches of autobahn may have higher signposted limits. Towing is limited to 80kmh unless a Tempo 100 has been obtained from the authorities. Larger motorhomes over 3,500kg: 80/80/80 and 80/60/60 if towing.
Belgium
Lower car speed limits on Flemish region other roads of 70kmh. Other areas: 120/90/90. No specific information on towing of larger motorhomes.
Italy
Cars: 130/110/90. Towing: 80/70/70. Large motorhomes over 3,500kg: 100/80/80.
Compulsory speed stickers
Italy requires all caravans to have two different stickers: 70 and 80 (the kmh limits for speeds outside built-up areas and highways).
For motorhomes the stickers are only compulsory if the total mass exceeds 3,500kg. Up to 12,000kg the stickers required are 80 and 100.
Luxembourg
Cars: 130/NA/90. Towing: 90/NA/75. No clear advice for larger motorhomes.
Denmark
Cars: 110/80/80. Towing: 80/70/70. Motorhomes over 3,500kg: 70/70/70. For cars, speed limit may be 130kmh on certain signposted stretches of motorway.
Switzerland
Cars: 120/80/80. Motorhomes over 3,500kg: 100/80/80. No towing advice.
Stay road smart
Always follow local signage and advice as the above list is not exhaustive and should be treated as a guide only – it is also subject to change by each country’s authorities. Some countries do not provide specific information for towing so speed limits may be the same as for cars.
Road tolls
When planning your route(s), be aware that there are numerous toll roads across the whole of Europe, as well as in the UK. More information about UK toll roads is available here. If travelling via the Channel Tunnel or Dover via the Dartford Crossing, please note that toll booths are no longer in operation, and you need to pay via here.
There are some useful websites to find out more about toll roads in mainland Europe including, Tolls.EU, and Tolltickets, and a toll route calculator called Tollguru, which also has an App. Please note we suggest you use these sites for research purposes only, as they will charge a premium on top of the fees charged by the official toll road websites, which can be easily found using an internet search engine.
There is normally a simple system to pay as you go or buy preloaded cards depending on the system used by the toll road operator. Free flowing systems are increasingly being introduced, which can involve a pre-registered account and vehicle recognition or via an app. Many toll websites have route planning tools that can help determine toll charges for your chosen route.
Toll tags
Many toll roads have special lanes with electronic tolls that have no toll booths, and the passage of vehicles is detected by means of electronic gateways and tags within the vehicle. These use an automatic device for vehicles up to 3m high and 3,500kg in weight affixed to the windscreen and are valid for all toll motorways in France, Spain and Portugal, and Italy. Opting to use these devices will speed up your passage through toll collection areas. If they do not suit you or your unit, simply pay as you go at the toll booths. More information is available here.
 Tags help to speed up travel through toll collection areas
Tags help to speed up travel through toll collection areas
Some specific country toll information is listed below:
Portugal
Portugal Tolls explains the various ways to pay. Portuguese motorways that use the electronic toll system have no traditional toll booths, and British number plates are recognised by the system.
The simplest way to pay is to check on the website how much it will cost, and then buy pre-paid toll cards for that amount, which are normally valid for 30 days from activation. These are available at service stations near the toll roads and border crossings. To decide how many pre-paid toll cards to buy, visit the website first.
Additional information can be found here.
France and Spain
Many motorways in France and Spain (known as Autoroutes and Autopistas respectively) charge a toll fee. Toll roads are identified by the word ‘peage’ in French and ‘peaje’ in Spanish. A ticket is taken on joining the road at the toll booth and then handed over at the next toll booth on the journey, where payment will be required by cash or bank card. The toll gates are often automated, so you can simply insert your ticket, followed by your credit card, and then collect a receipt.
More information for French motorways and tolls can be found at Autoroutes and Sanef and for Spanish motorways at Autopistas.
Emission zones and congestion charges
Low Emission Zones (LEZs) and Clean Air Zones (CAZs) are being introduced across the whole of Europe, to discourage more polluting vehicles from entering built-up areas and reduce harmful emissions. Some cities also have congestion charging schemes to help reduce the volume of traffic.
It's important to consider how all this will affect your travel around mainland Europe. The Urban Access Regulation in Europe website contains a variety of useful information, including maps, any requirement to display stickers on your vehicle such as Crit’Air in France, and links to official sources where necessary. You should also visit the UK Government official website to find out about UK emission zones you may pass through on your chosen route, as well as the emission status of your vehicle, which can be obtained by entering its registration number.
A smart device app called Green Zones, which contains live information and maps, can also be helpful while on the move.
 In France a red circle sign denotes an emission zone, with the Crit’Air classes underneath
In France a red circle sign denotes an emission zone, with the Crit’Air classes underneath
Compulsory items and other legal requirements
Different countries have different rules about the items and equipment you must carry in your vehicle – as well as what’s prohibited – so make sure to check in advance. If you are missing any piece of equipment required by law, you could be subject to a fine if stopped by the authorities. We therefore highly recommend that you carry the following items, whether compulsory or not:
- Passport
- Original vehicle registration document V5C or VE103B (for lease vehicle) or Vehicle on Hire Certificate
- Driving licence and IDP
- Vehicle insurance document and breakdown cover if applicable
- A Green card may be needed for certain countries
- Travel documents and EHIC/GHIC
- AHC (if you’re travelling with a pet)
- Environmental badges or stickers (if needed)
- Two warning triangles
- UK sticker on vehicle and any trailer
- First aid kit
- Check vehicle handbook for advice on adjustment of headlights or need for headlamp beam deflectors
- Reflective jacket or waistcoat for every occupant to EU standard EN471. These must be worn in Spain when exiting the car on public roads outside built-up areas
- Blind spot stickers for vehicles over 3,500kg (see below)
Refer to the Touring in mainland Europe guide for more detail about paperwork required for travel.
Blind spot stickers
If you are travelling through France in a vehicle with a maximum authorised mass of more than 3,500kg you will need to display a blind-spot sticker known as Angles Morts. This means larger motorhomes will need to display these stickers at defined positions or face a fine.
It may also apply to larger fifth wheel units if the tow vehicle is over 3,500kg. More information can be found on the French Government website.
Breathalyser kits
The law requiring drivers to carry a breathalyser kit in France was repealed in 2020, so it is no longer a legal requirement to carry them in your vehicle. That said, the drink drive limit in the UK is the joint highest in Europe, so keeping a breathalyser kit in the vehicle may be considered useful by some when driving abroad. The Club advises never to drink and drive.
Reflective plates (Spain)
When travelling in Spain, a motorhome or car and caravan combination over 12m shipping length requires a yellow reflective plate 1,300mm long and 250mm high, edged with a 40mm wide red fluorescent band (manufactured to ECE70 standard).
This plate may be replaced by two of similar design, 500mm long and 250mm high, situated symmetrically at the rear of the vehicle and as near to the edge as possible.
The plates must be positioned between 500mm and 1,500mm from the ground. These can be ordered online at HGV Direct.
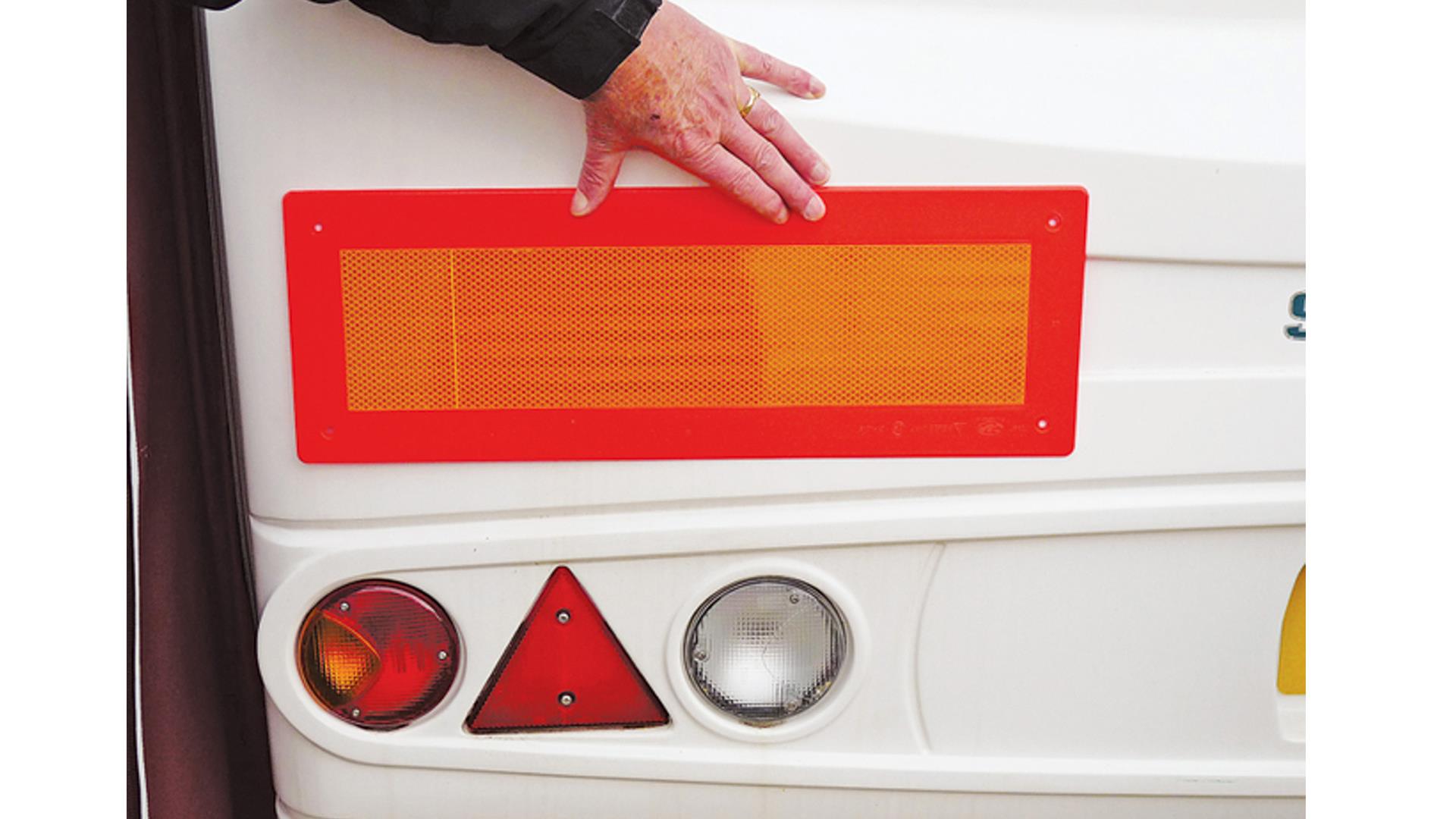 A reflective plate is required in Spain
A reflective plate is required in Spain
Rear loads on vehicles or caravans
Many of the regulations around carrying rear loads fall under common rules and these are:
- A reflective red and white striped hazard sign should be attached to cycles or other items carried at the rear of your vehicle or outfit. Typically, these are 50cm x 50cm
- The carrying device and the load must not restrict the visibility of the lights, signals or number plate
- Bicycles may be carried at the rear of a car, motorhome, camper van or caravan (see specific requirements below)
- Loads should not protrude beyond the front of the vehicle or trail on the ground
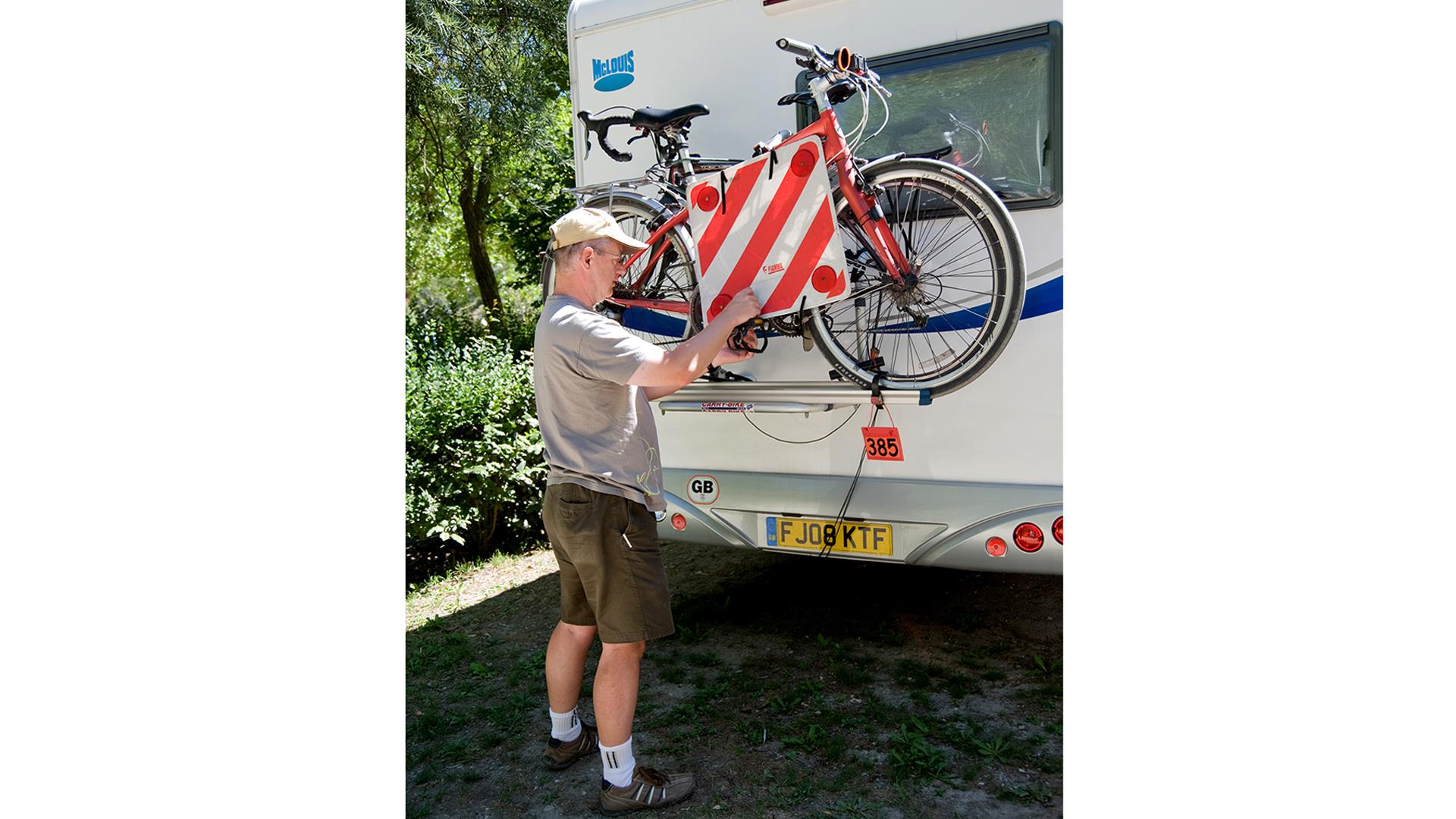 Rear loads should be clearly identified and not obscure road lights or the registration plate
Rear loads should be clearly identified and not obscure road lights or the registration plate
Each country may have specific requirements, some common ones are listed below:
Spain
- Rear loads must not exceed 10 per cent of the length of the vehicle (15 per cent in the case of indivisible items)
- For a vehicle that is towing, any load-carrying device must not rest on the towbar itself. This could be interpreted as towball-mounted bike racks used while towing being prohibited
Portugal
- Loads must not project beyond the width of the vehicle
France
- Rear loads must not exceed 3m beyond the rear extremity of the vehicle or its trailer
Towing cars behind motorhomes
Towing a motor vehicle on its wheels is generally prohibited in the EU, except in the case of a breakdown or an accident and only if the distance to be travelled is short. The practice is banned on motorways, where you must seek the assistance of a recovery vehicle. However, it is legal to tow a car on a trailer where none of its wheels are on the road.
More information about towing cars behind motorhomes while abroad can be found in the Expert Guide: Towing with a motorhome.
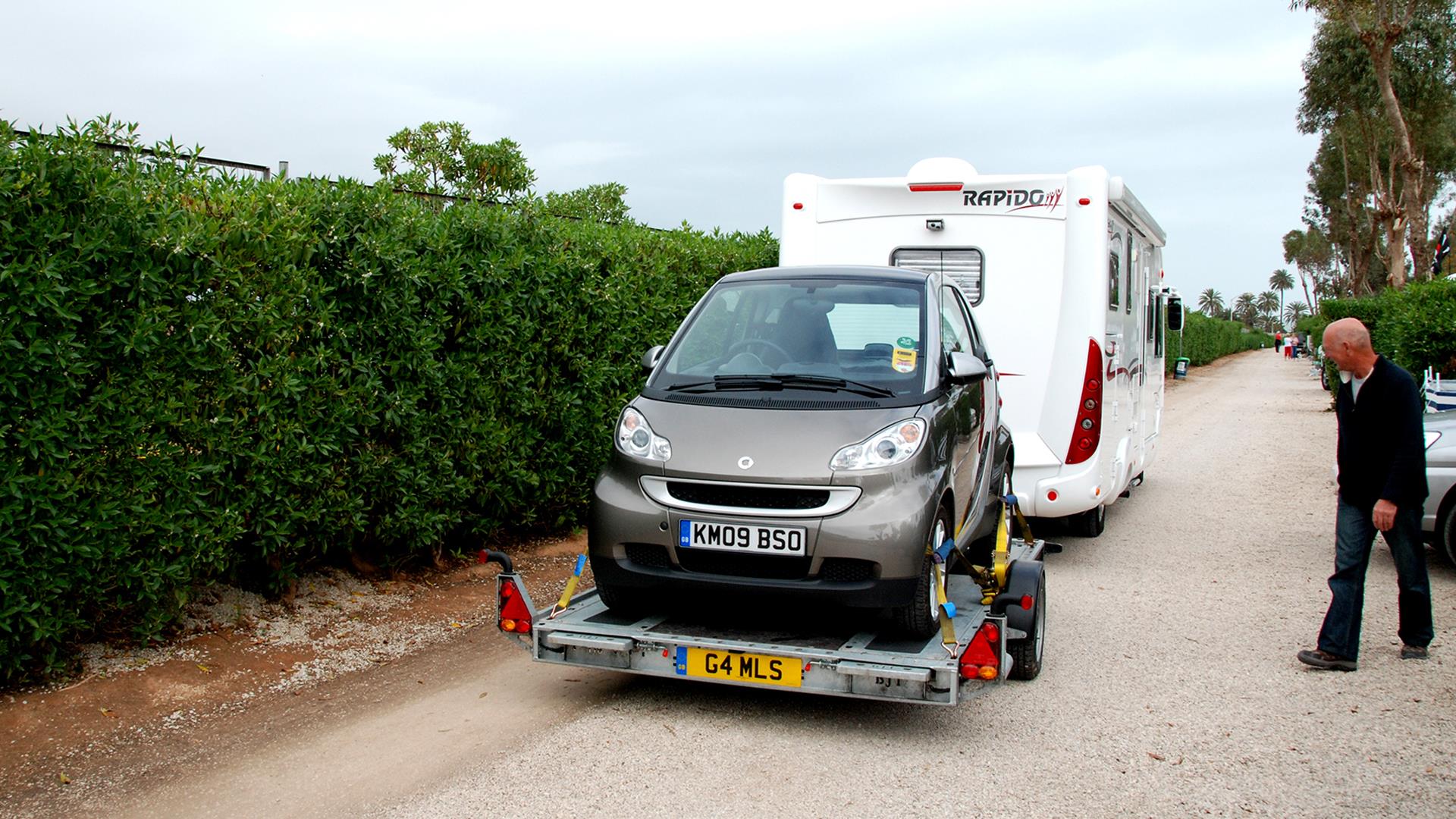 It’s legal to tow a car or motorbike on a trailer where none of its wheels are on the road
It’s legal to tow a car or motorbike on a trailer where none of its wheels are on the road
Cameras
Safety camera detectors or locations within satnav maps
Point Of Interest (POI) radar detectors that show the precise position of speed cameras, are generally forbidden across Europe. This function can be deactivated on most satnavs.
Satnav systems showing areas known as safety zones, where there may be speed cameras, are generally permitted in France, Spain, Belgium and Italy. In Germany, these POIs must be deactivated.
Dash cameras
While many UK motorists have installed dashboard cameras (dash cams) to track their own journey, and for use as evidence in the event of an accident, the RAC has advised that in countries with strict privacy laws such as Switzerland, Portugal and Austria, the use of dash cams is banned. Other countries including Belgium, Germany and France allow these cameras for private use only, meaning the content they capture should not be uploaded to social media or websites.
 Up-to-date maps on satnavs are very useful but check the rules for speed cameras
Up-to-date maps on satnavs are very useful but check the rules for speed cameras
